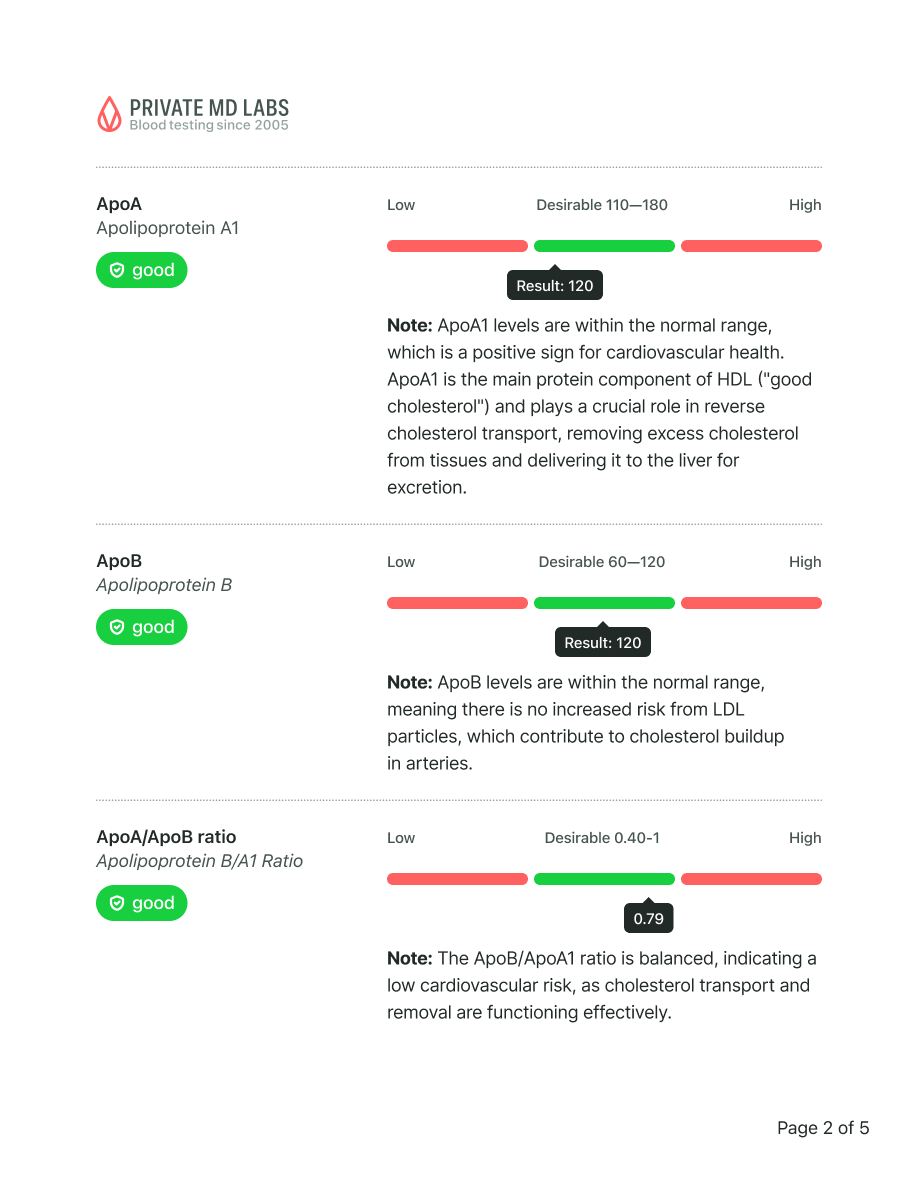
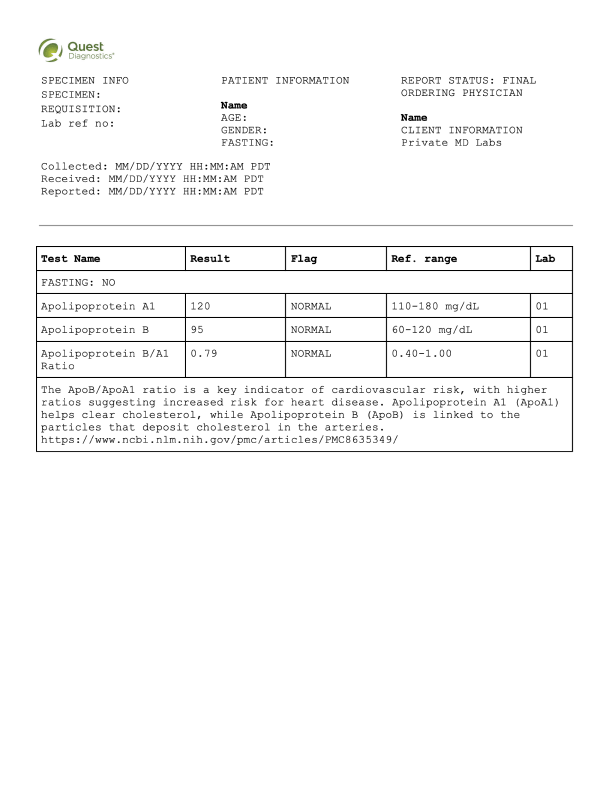
Sample results
Aplastic anemia is a rare but serious blood disorder where the bone marrow fails to produce sufficient new blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It is caused by damage to the bone marrow stem cells from autoimmune disorders, radiation, chemotherapy, toxic chemicals, certain medications, or viral infections like hepatitis. The White Blood Cell Count (WBC) is the most important test for diagnosis because it detects the low white blood cell levels characteristic of this bone marrow failure condition.
 90-day money-back guarantee
90-day money-back guarantee
 Lab order in minutes
Lab order in minutes
 Save a trip to the doctor
Save a trip to the doctor
 Low prices since 2005
Low prices since 2005
 Labs within 2 miles
Labs within 2 miles
Aplastic anemia is caused by damage to the bone marrow stem cells that produce blood cells. The most common causes include autoimmune disorders where the immune system attacks the bone marrow, exposure to toxic chemicals like benzene and pesticides, radiation and chemotherapy treatments, certain medications including some antibiotics and anticonvulsants, and viral infections such as hepatitis, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, and HIV. In about half of cases, the exact cause cannot be identified, which is called idiopathic aplastic anemia.
The White Blood Cell Count (WBC) is the most important test for aplastic anemia because it detects the critically low white blood cell levels that occur when bone marrow fails to produce new cells. This test is typically performed as part of a Complete Blood Count (CBC) that also measures red blood cells and platelets, which are also reduced in aplastic anemia. The characteristic finding is pancytopenia, meaning all three blood cell types are low. Your doctor will also likely order a reticulocyte count to check for young red blood cells and may recommend a bone marrow biopsy to confirm the diagnosis by examining the bone marrow directly for reduced cell production.
You should get tested if you experience persistent fatigue and weakness that interferes with daily activities, frequent or unusual infections that do not respond well to treatment, unexplained bruising or bleeding including nosebleeds or bleeding gums, small red or purple spots on the skin called petechiae, rapid or irregular heartbeat, pale skin or shortness of breath with minimal exertion, or prolonged bleeding from cuts. These symptoms occur because your body lacks sufficient blood cells to carry oxygen, fight infections, and clot blood properly. Seek immediate testing if you develop fever with infection signs or uncontrolled bleeding, as aplastic anemia can become life-threatening without treatment.
 Save a trip to the doctor, go directly to the lab
Save a trip to the doctor, go directly to the lab
 Instant orders, results often overnight*
Instant orders, results often overnight*
 Results explained in simple language
Results explained in simple language
 Reviewed by US licensed doctors
Reviewed by US licensed doctors
 Fast & confidential, we never sell or share your data
Fast & confidential, we never sell or share your data
 No insurance needed, transparent pricing
No insurance needed, transparent pricing
What this means
Your testosterone levels are slightly below the optimal range. While this is not necessarily cause for concern, it may contribute to occasional fatigue, reduced motivation, or lower muscle mass over time.
Recommended actions
Increase resistance or strength training
Prioritize 7–8 hours of quality sleep per night, try to reduce stress
Include more zinc- and magnesium-rich foods (like shellfish, beef, pumpkin seeds, spinach)
Consider retesting in 3–6 months
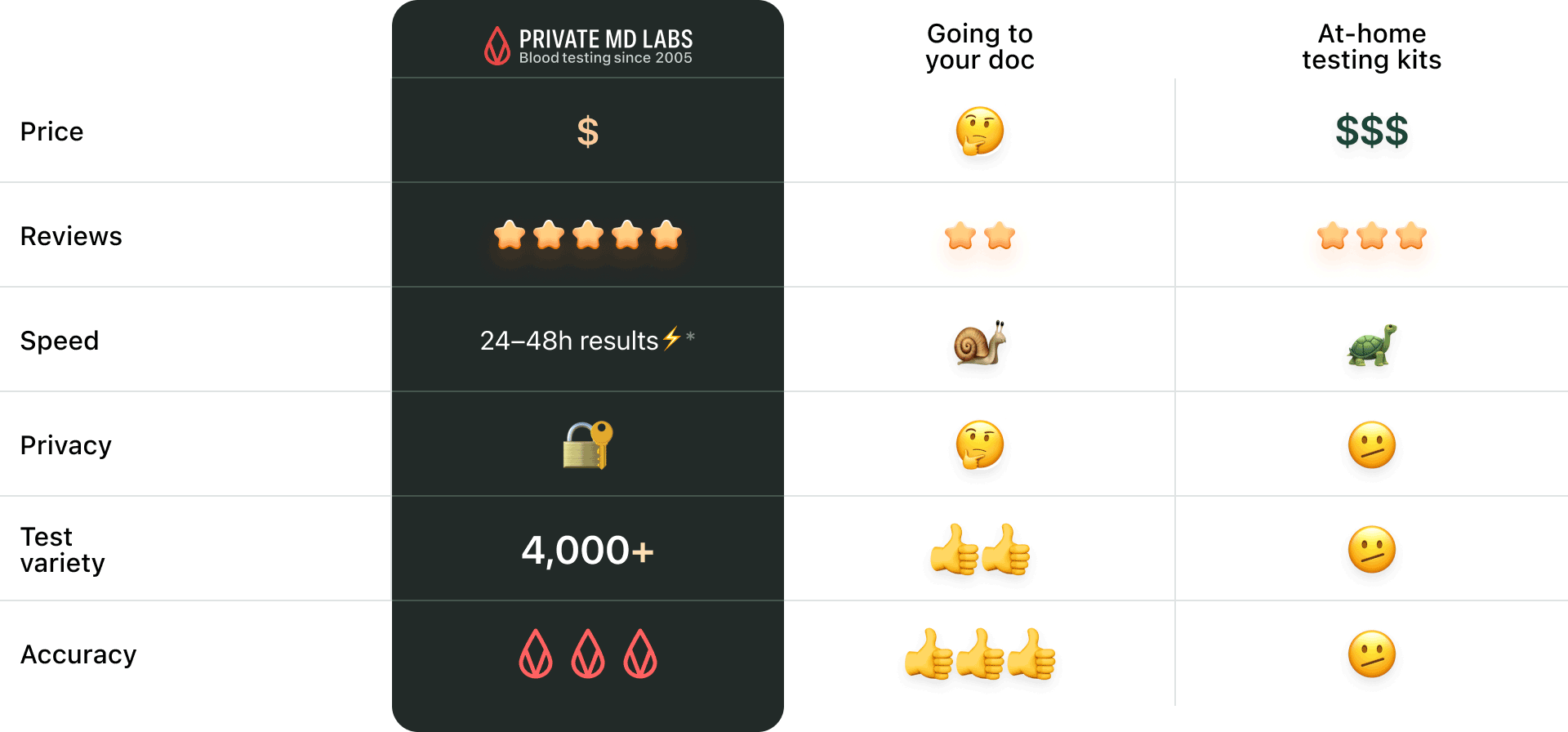
Not overhyped or overpriced. Just comprehensive blood testing made simple and for everyone.







Sample results


Your 24/7 Personal Lab Guide
Quick questions: