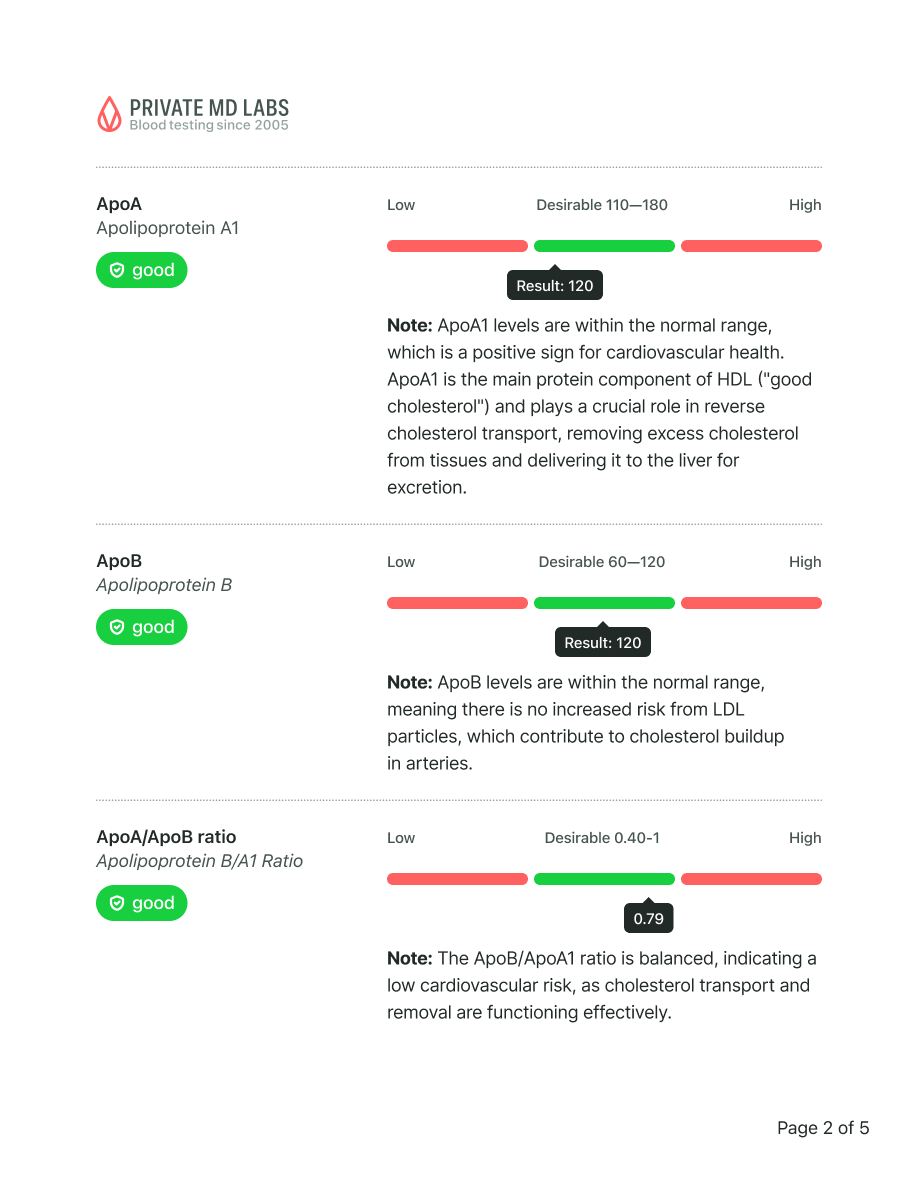
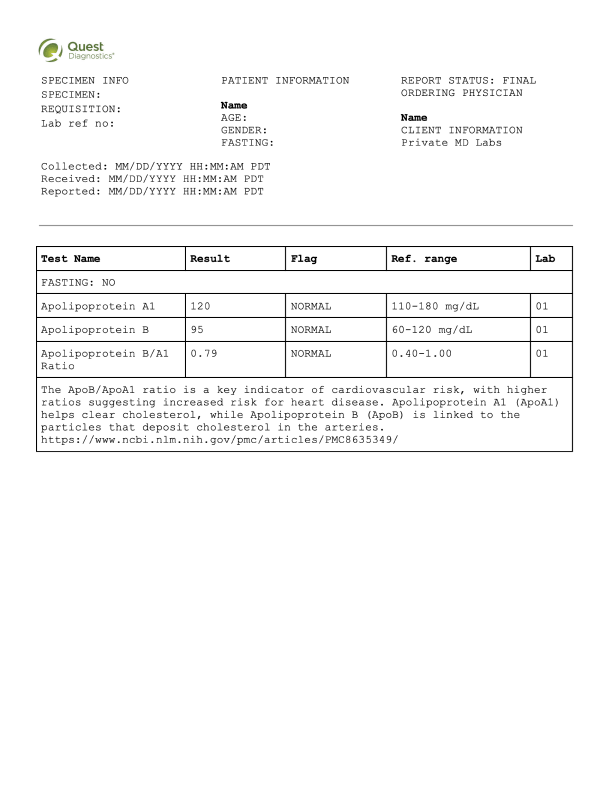
Sample results
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) deficiency is an endocrine disorder where the pituitary gland fails to produce sufficient ACTH. It is caused by pituitary gland dysfunction that prevents adequate stimulation of the adrenal glands to produce cortisol. The Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) test is the most important test for diagnosis because it directly measures ACTH levels in the blood.
 90-day money-back guarantee
90-day money-back guarantee
 Lab order in minutes
Lab order in minutes
 Save a trip to the doctor
Save a trip to the doctor
 Low prices since 2005
Low prices since 2005
 Labs within 2 miles
Labs within 2 miles
ACTH deficiency is caused by pituitary gland dysfunction that prevents the gland from producing adequate amounts of adrenocorticotropic hormone. This can result from pituitary tumors, traumatic brain injury, radiation therapy to the brain, surgical removal of pituitary tissue, infections affecting the pituitary gland, or autoimmune conditions. Without sufficient ACTH production, the adrenal glands receive inadequate signals to produce cortisol, leading to symptoms like chronic fatigue, muscle weakness, weight loss, and dangerously low blood pressure.
The Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) test is the most important test for ACTH deficiency because it directly measures the level of ACTH circulating in your bloodstream. This test detects whether your pituitary gland is producing enough ACTH to stimulate cortisol production by the adrenal glands. Low ACTH levels confirm the diagnosis and help distinguish pituitary-related deficiency from primary adrenal insufficiency. Your healthcare provider may also order a cortisol test alongside the ACTH test to see how low ACTH levels are affecting your adrenal function and cortisol production.
You should get tested if you experience persistent fatigue that does not improve with rest, unexplained muscle weakness, dizziness or fainting episodes related to low blood pressure, unexpected weight loss without trying, or darkening of the skin in certain areas. Testing is especially important if you have a history of pituitary problems, brain injury, brain surgery, or radiation therapy to the head, as these conditions significantly increase your risk. Early diagnosis through blood testing helps prevent serious complications like adrenal crisis and guides appropriate hormone replacement therapy.
 Save a trip to the doctor, go directly to the lab
Save a trip to the doctor, go directly to the lab
 Instant orders, results often overnight*
Instant orders, results often overnight*
 Results explained in simple language
Results explained in simple language
 Reviewed by US licensed doctors
Reviewed by US licensed doctors
 Fast & confidential, we never sell or share your data
Fast & confidential, we never sell or share your data
 No insurance needed, transparent pricing
No insurance needed, transparent pricing
What this means
Your testosterone levels are slightly below the optimal range. While this is not necessarily cause for concern, it may contribute to occasional fatigue, reduced motivation, or lower muscle mass over time.
Recommended actions
Increase resistance or strength training
Prioritize 7–8 hours of quality sleep per night, try to reduce stress
Include more zinc- and magnesium-rich foods (like shellfish, beef, pumpkin seeds, spinach)
Consider retesting in 3–6 months
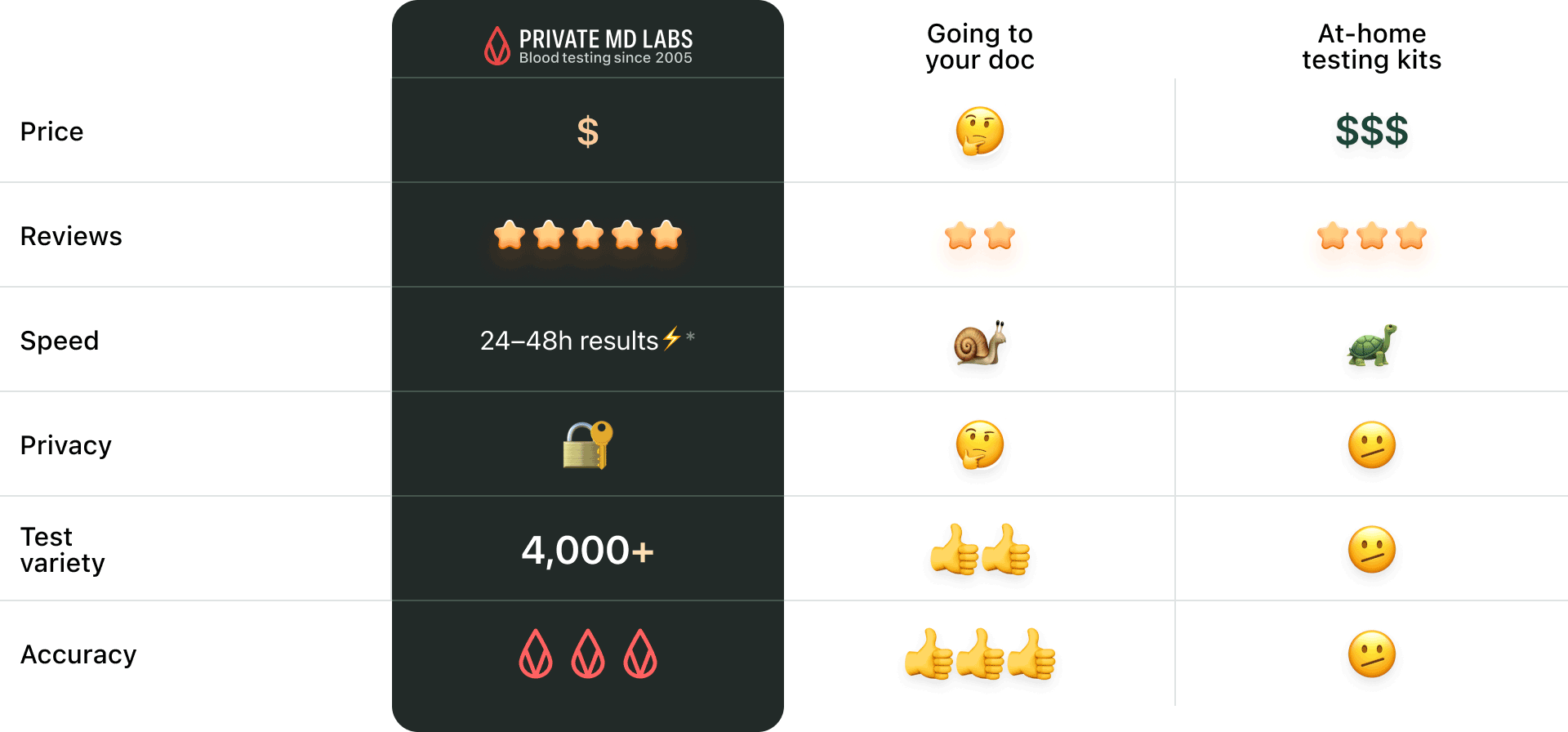
Not overhyped or overpriced. Just comprehensive blood testing made simple and for everyone.







Sample results


Your 24/7 Personal Lab Guide
Quick questions: