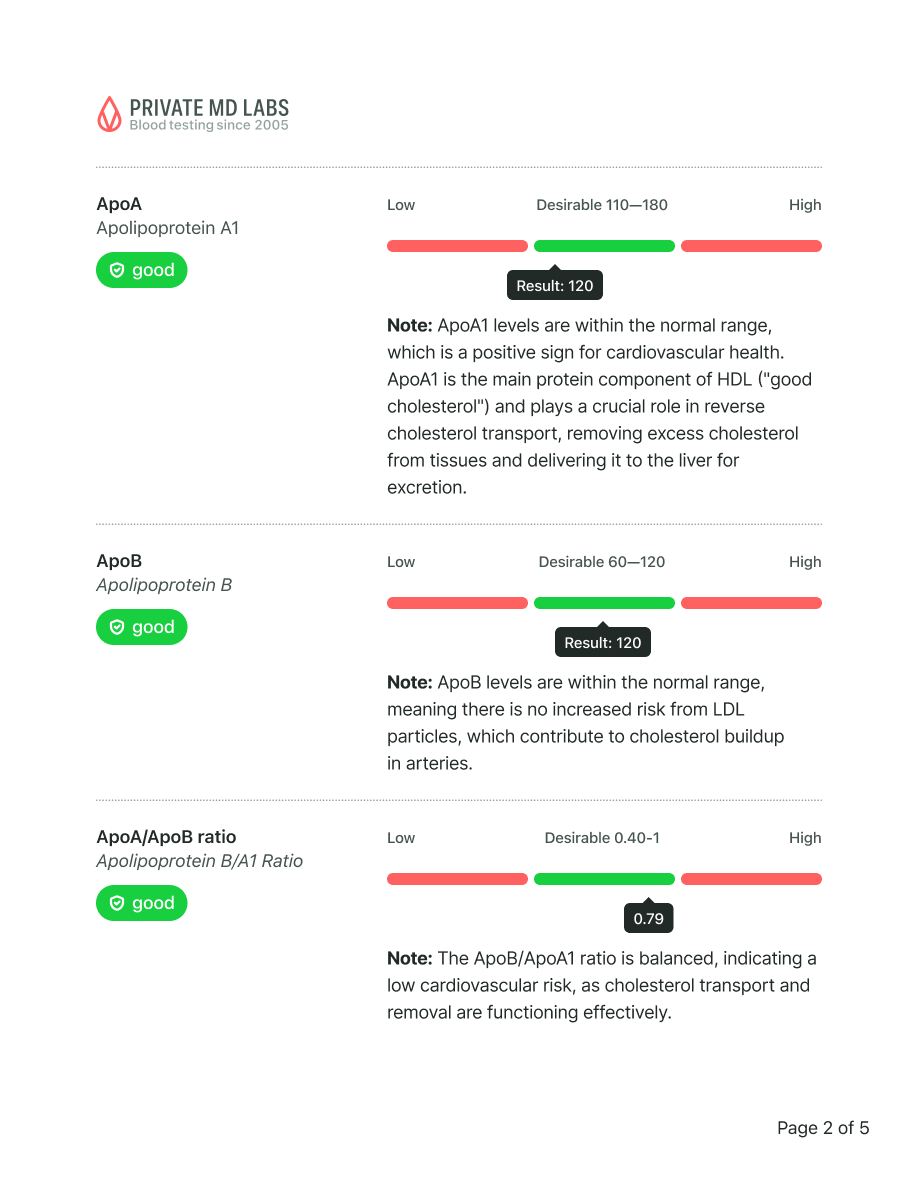
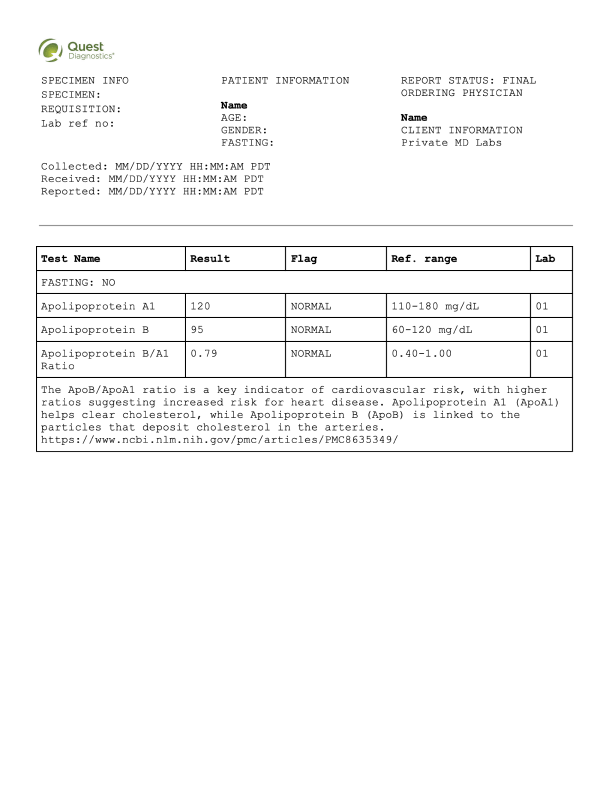
Sample results
Acute HIV syndrome is the earliest stage of HIV infection that occurs 2-4 weeks after exposure to the virus. It is caused by rapid replication of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus throughout the body, resulting in extremely high viral loads. The HIV 1/2 Antigen and Antibodies Fourth Generation test is the most important test for diagnosis because it detects both viral antigens and antibodies during this critical early phase.
 90-day money-back guarantee
90-day money-back guarantee
 Lab order in minutes
Lab order in minutes
 Save a trip to the doctor
Save a trip to the doctor
 Low prices since 2005
Low prices since 2005
 Labs within 2 miles
Labs within 2 miles
Acute HIV syndrome is caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1 or HIV-2) entering the body and rapidly multiplying throughout the bloodstream and lymphatic system. After initial exposure through sexual contact, blood exposure, or needle sharing, the virus attacks CD4+ T cells, which are critical components of the immune system. During this acute phase, which occurs 2-4 weeks after infection, viral replication is at its peak, producing extremely high concentrations of the virus in the blood and making this the most contagious stage of HIV infection.
The HIV 1/2 Antigen and Antibodies Fourth Generation test is the most important test for acute HIV syndrome because it detects both HIV antigens (specifically the p24 antigen protein produced by the virus) and HIV antibodies simultaneously. This dual detection capability is essential during acute infection because viral antigens appear in the blood 1-3 weeks before antibodies develop, providing a critical early detection window. Fourth-generation testing can identify HIV infection as early as 2-4 weeks after exposure, significantly earlier than older antibody-only tests, allowing for prompt initiation of antiretroviral therapy during this highly infectious stage.
You should get tested if you have had unprotected sexual contact, shared needles, or had any potential exposure to HIV within the past 2-6 weeks, especially if you are experiencing flu-like symptoms such as fever, sore throat, rash, swollen lymph nodes, or extreme fatigue. Testing is also essential if a sexual partner has disclosed their HIV-positive status or if you have experienced occupational exposure through needlestick injuries. Because acute HIV syndrome represents the most contagious stage with the highest viral loads, early testing within 2-4 weeks of potential exposure is critical for starting treatment quickly and preventing transmission to others.
 Save a trip to the doctor, go directly to the lab
Save a trip to the doctor, go directly to the lab
 Instant orders, results often overnight*
Instant orders, results often overnight*
 Results explained in simple language
Results explained in simple language
 Reviewed by US licensed doctors
Reviewed by US licensed doctors
 Fast & confidential, we never sell or share your data
Fast & confidential, we never sell or share your data
 No insurance needed, transparent pricing
No insurance needed, transparent pricing
What this means
Your testosterone levels are slightly below the optimal range. While this is not necessarily cause for concern, it may contribute to occasional fatigue, reduced motivation, or lower muscle mass over time.
Recommended actions
Increase resistance or strength training
Prioritize 7–8 hours of quality sleep per night, try to reduce stress
Include more zinc- and magnesium-rich foods (like shellfish, beef, pumpkin seeds, spinach)
Consider retesting in 3–6 months
Not overhyped or overpriced. Just comprehensive blood testing made simple and for everyone.
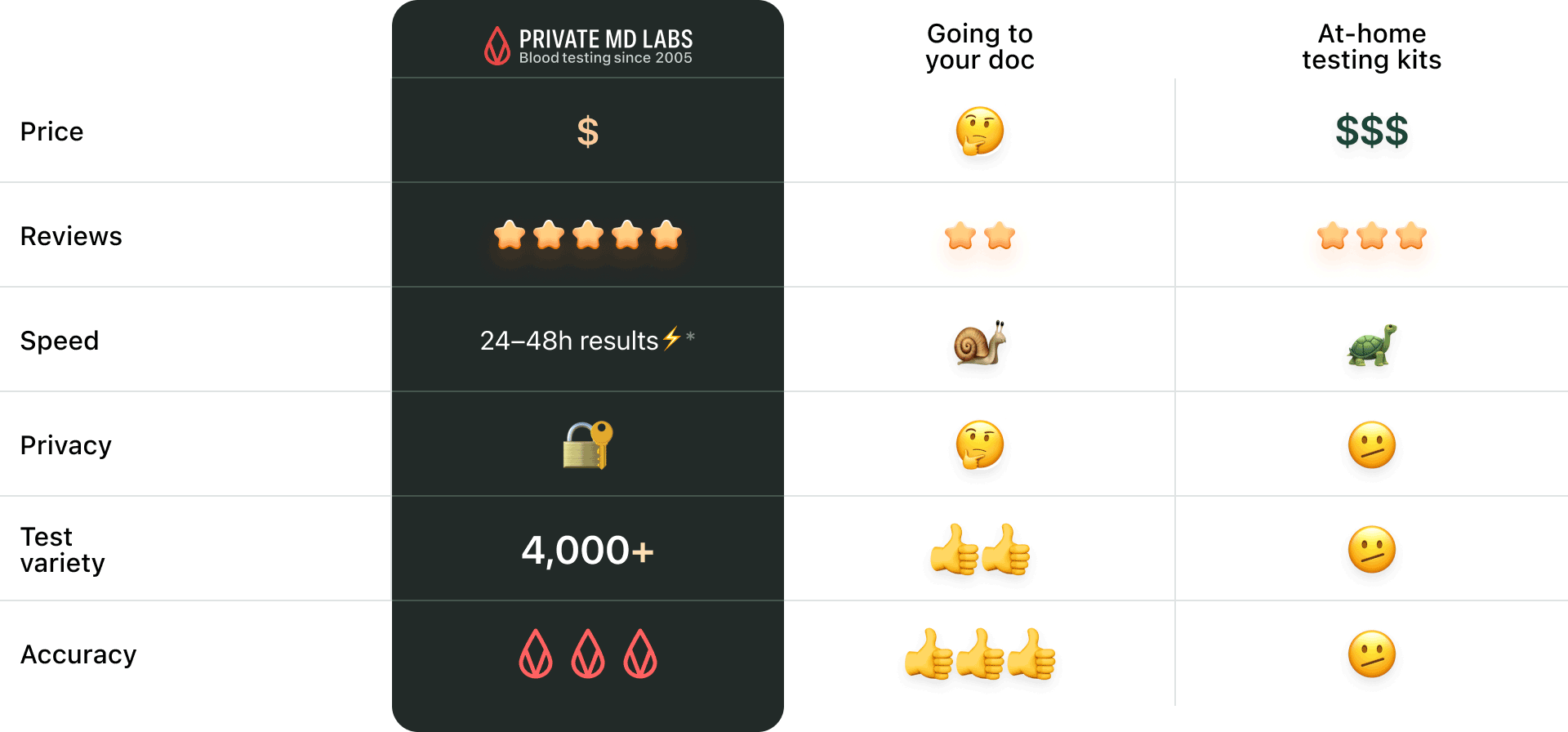







Sample results


Your 24/7 Personal Lab Guide
Quick questions: