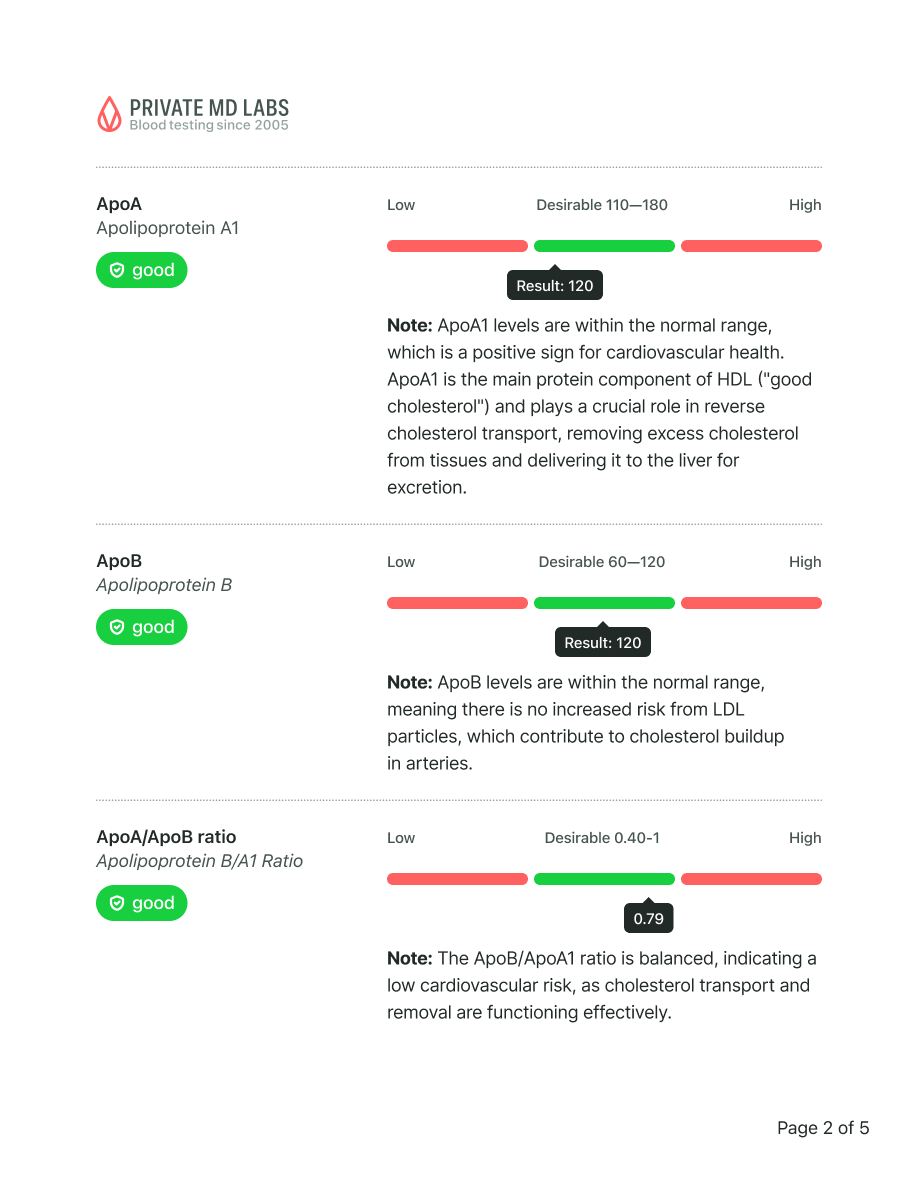
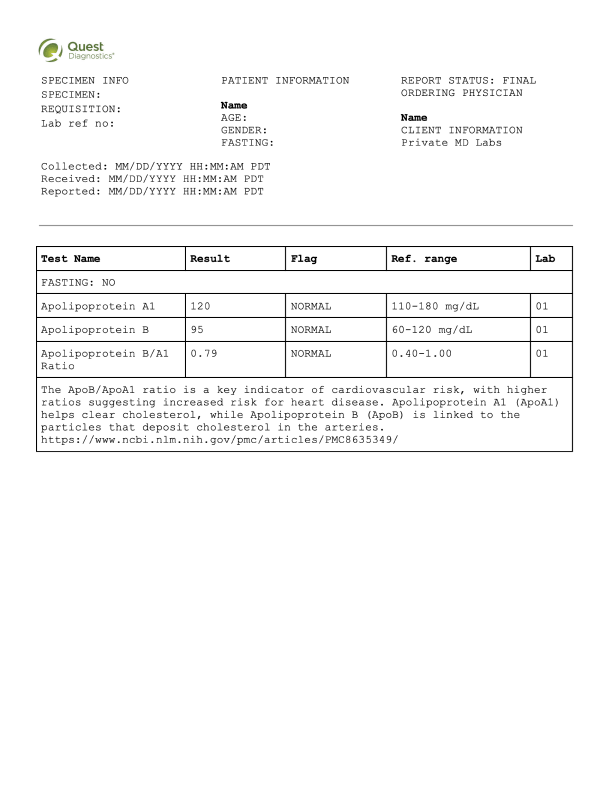
Sample results
Acute Hepatitis B infection is a viral liver disease that develops within the first 6 months after exposure to the Hepatitis B virus (HBV). It is caused by the Hepatitis B virus, which is transmitted through contact with infected blood, semen, or other bodily fluids. The Hepatitis B Core Antibody IgM test is the most important test for diagnosing acute Hepatitis B infection because it specifically detects antibodies produced during recent infection.
 90-day money-back guarantee
90-day money-back guarantee
 Lab order in minutes
Lab order in minutes
 Save a trip to the doctor
Save a trip to the doctor
 Low prices since 2005
Low prices since 2005
 Labs within 2 miles
Labs within 2 miles
Acute Hepatitis B infection is caused by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV), which enters your body through contact with infected blood, semen, vaginal fluids, or other bodily fluids. The virus spreads through activities like unprotected sex with an infected person, sharing needles or syringes, accidental needle sticks in healthcare settings, or from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth. Unlike chronic Hepatitis B, acute infection occurs when your body is first exposed to the virus and typically develops symptoms within 1 to 4 months after exposure.
The Hepatitis B Core Antibody IgM test is the most important test for diagnosing acute Hepatitis B infection because it specifically detects the IgM antibodies your immune system produces during a recent or ongoing infection. This antibody typically appears within 4 to 6 weeks after you are exposed to the virus and remains detectable for about 6 months, making it an excellent marker that distinguishes acute infection from past or chronic infection. The test can detect the infection even during the window period when other markers might not yet be present in your blood, ensuring accurate early diagnosis that is critical for proper treatment and preventing transmission to others.
You should get tested if you have been exposed to someone with Hepatitis B, had unprotected sex with a new or multiple partners, shared needles or drug equipment, or experienced an accidental needle stick. Testing is also important if you notice symptoms like yellowing of your skin or eyes, dark urine, extreme fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, or loss of appetite. Healthcare workers, pregnant women, and people living with someone who has Hepatitis B should also get tested regularly. Early detection allows for prompt medical care and helps prevent spreading the virus to others.
 Save a trip to the doctor, go directly to the lab
Save a trip to the doctor, go directly to the lab
 Instant orders, results often overnight*
Instant orders, results often overnight*
 Results explained in simple language
Results explained in simple language
 Reviewed by US licensed doctors
Reviewed by US licensed doctors
 Fast & confidential, we never sell or share your data
Fast & confidential, we never sell or share your data
 No insurance needed, transparent pricing
No insurance needed, transparent pricing
What this means
Your testosterone levels are slightly below the optimal range. While this is not necessarily cause for concern, it may contribute to occasional fatigue, reduced motivation, or lower muscle mass over time.
Recommended actions
Increase resistance or strength training
Prioritize 7–8 hours of quality sleep per night, try to reduce stress
Include more zinc- and magnesium-rich foods (like shellfish, beef, pumpkin seeds, spinach)
Consider retesting in 3–6 months
Not overhyped or overpriced. Just comprehensive blood testing made simple and for everyone.
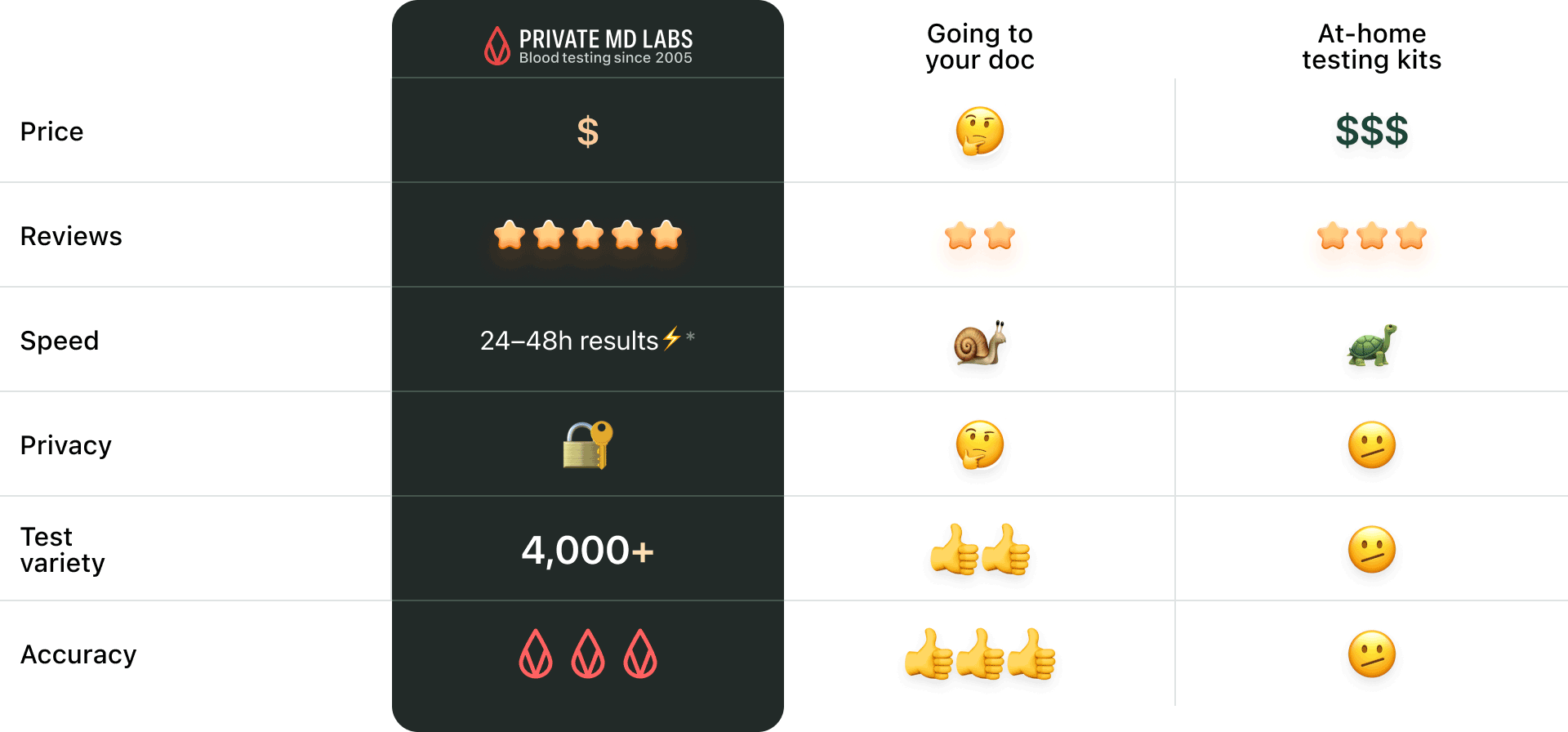







Sample results


Your 24/7 Personal Lab Guide
Quick questions: